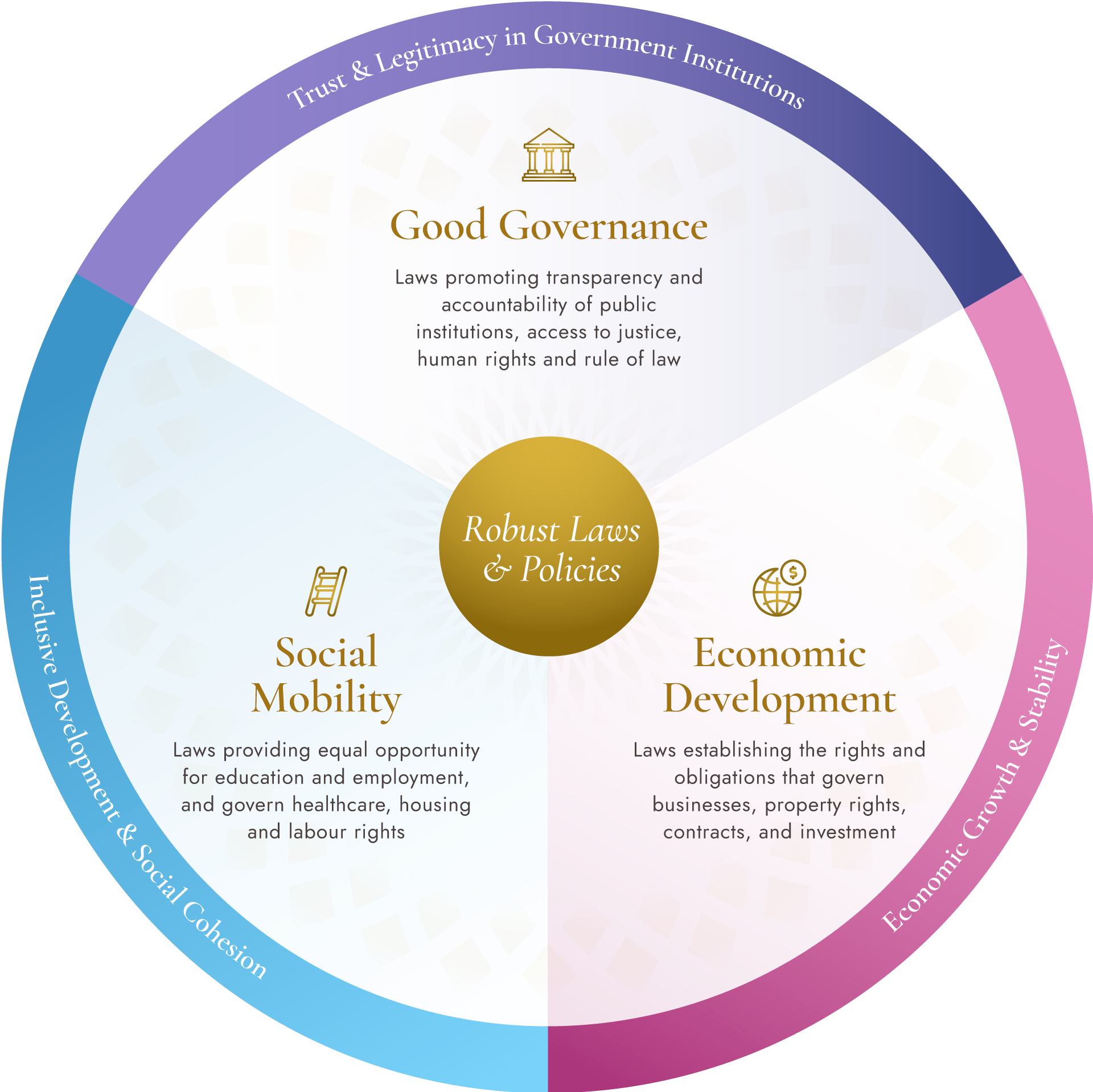
The Chandler Law and Development Model (LDM)
History and empirical research show that effective laws and policies are instrumental in building strong, prosperous nations. The Chandler Law and Development Model (LDM) provides a holistic framework for guiding the law reform process, emphasising the interconnectedness of national governance, economic development, and social mobility.
Through strategic initiatives to develop effective legal frameworks in these three focus areas, CIJ works with national leaders, lawmakers, and legislative bodies to build resilient societies founded on the principles of justice, equity, and prosperity.
Good Governance
Good governance is characterised by adherence to the rule of law, transparency, accountability, and respect for human rights, all of which are enshrined in legal frameworks.
Legal frameworks establish the institutional mechanisms and checks and balances necessary to prevent abuse of power, corruption, and arbitrary decision-making.
An independent judiciary, robust legal institutions, and effective enforcement mechanisms are essential components of good governance, ensuring that laws are applied impartially and citizens’ rights are protected.
Transparent and accountable governance practices build trust in institutions, promote economic stability, and attract investment, contributing to long-term economic growth.
Economic Development
Robust laws uphold property rights and create a reliable, trustworthy framework for entering into contracts, dispute resolution, and investments.
Insecure property rights destroy the incentives for investment, innovation, and entrepreneurship. Strong legal frameworks that uphold property rights, including intellectual property rights, are thus essential to economic development.
Effective legal systems include safeguards for investments and create the means for upholding contract terms and resolving disputes. These factors encourage investor confidence and improve access to capital for the country’s businesses.
Access to employment opportunities, decent wages, and social services contribute to poverty reduction, social mobility, and improved standards of living.
Social Mobility
Strong legal frameworks protect fair access to housing and public services and uphold the principle of non-discrimination, delivering equality of opportunity.
The impartial application of just laws ensures that all people have recourse to the law without fear of discrimination, mistreatment, or bias. This protects the rights of marginalised groups and fosters social cohesion.
Laws governing education, healthcare, housing, labour rights, and social protection contribute to the wellbeing and prosperity of individuals and communities, addressing inequalities.
Strong legal frameworks that encourage economic development, the principle of non-discrimination, and equal access to basic public goods improve equality of opportunity and generate greater chances for people of all backgrounds to achieve social mobility.